Net Zero Water
Net Zero Water practices represent a revolutionary approach to sustainable living and environmental stewardship. By harnessing techniques such as water harvesting, collection, storage, and filtration, along with the separation and composting of grey and black water, Net Zero Water Systems aim to create a self-sustaining water ecosystem.
This method not only meets the water needs of both human occupants and food forests or living roofs, but also significantly reduces the demand on local water resources. The benefits of adopting a Net Zero Water strategy are multifaceted, contributing to both ecological health and resource efficiency.
Firstly, Net Zero Water systems dramatically decrease the consumption of potable water by recycling greywater for irrigation and other non-potable uses. This not only conserves precious freshwater resources but also reduces the strain on municipal water and sewage treatment facilities.
By filtering and reusing greywater, these systems ensure that every drop of water serves multiple purposes before it is returned to the environment, thereby minimizing waste. Furthermore, the separation and composting of blackwater into nutrient-rich compost not only diverts waste from sewage systems but also provides an excellent source of natural fertilizer for food forests, closing the loop on waste and resource use.
In regions facing water scarcity, Net Zero Water practices offer a sustainable solution that can alleviate pressure on water supplies and contribute to the resilience of local communities against droughts and water shortages. Through the integration of these innovative water management techniques, individuals and communities can take a significant step towards sustainability, self-sufficiency, and harmony with the natural environment.
Water: clean, grey, and black
Clean water, also known as potable water, is safe for consumption and comes from treated sources like wells and municipal systems.
Greywater comes from baths and kitchens, can be reused for irrigation after treatment.
Blackwater contains human waste, requires extensive treatment before it can be repurposed for non-potable uses or safely discharged.
About this Process
The journey toward achieving Net Zero Water is both a commitment to sustainability and a testament to human ingenuity in harmonizing with nature’s cycles.
This process is built on a foundation of innovative water management strategies that aim to create a self-sufficient, eco-friendly water system.
It encapsulates the essence of sustainability by ensuring that our water usage does not deplete the environment but instead contributes to its flourishing.



First Step: Complete the Project form
Core Principles
Sustainability:
At the heart of Net Zero Water is the principle of sustainability—using water resources in a way that meets current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs.
Efficiency:
This process is designed to maximize efficiency at every step, ensuring that every drop of water is captured, stored, treated, and used in the most effective way possible.
Recycling and Reuse:
Central to achieving Net Zero Water is the ethos of recycling and reuse, particularly through the innovative treatment of greywater and blackwater.
Environmental Stewardship:
The process embodies a deep respect for the natural world, aiming to reduce pollution, conserve resources, and enhance biodiversity.
Implementation Steps
1. Assessment:
The first step involves evaluating water needs and identifying potential sources of rainwater and greywater that can be harnessed.
2. System Design:
Tailored collection, storage, and treatment systems are designed to fit the specific needs and constraints of the household or community.
3. Installation and Maintenance:
Professional installation ensures optimal system performance, followed by regular maintenance to keep the system running efficiently.
4. Continuous Improvement:
As technologies advance and our understanding of sustainable practices deepens, the Net Zero Water process evolves, embracing innovations that enhance efficiency and sustainability.
Why It Matters
Embarking on the Net Zero Water process is more than just an environmental initiative; it’s a bold step towards redefining our relationship with the planet.
It demonstrates a commitment to preserving our most precious resource for ourselves and future generations, while also offering a blueprint for living in harmony with the Earth.
Through this process, we not only conserve water but also create a more resilient, sustainable, and healthy world.
Net Zero Water: A Sustainable Approach to Water Management
Introduction
In an era where water scarcity poses a significant threat to both the environment and human populations, the adoption of Net Zero Water practices offers a beacon of hope. Net Zero Water refers to a self-sufficient system that manages water resources by maximizing the collection, storage, and reuse of rainwater and greywater, while also responsibly handling blackwater. This innovative approach not only meets the water demands of human activities and agriculture but also contributes positively to the surrounding ecosystem.
How Net Zero Water Works
Net Zero Water systems are designed to capture rainwater and greywater (water from sinks, showers, and laundry), which are then filtered and stored for future use. This sustainable model also includes the separation and composting of blackwater (waste water from toilets) to produce nutrient-rich compost, further supporting agricultural efforts such as food forests.
- Water Harvesting and Collection:
By collecting rainwater through rooftop systems and other catchment methods, net zero water practices significantly reduce reliance on municipal water supplies. This harvested water can be stored in tanks for use during dry periods, ensuring a constant supply. - Storage and Filtration:
Advanced filtration systems are employed to purify greywater to a safe level for irrigation and other non-potable uses. This process extends the lifecycle of water, making every drop count. - Greywater and Blackwater Management:
Greywater is treated and reused for irrigation and, in some systems, for flushing toilets. Blackwater is carefully separated and treated through composting processes, transforming it into valuable compost for agriculture, thereby completing the nutrient cycle.
Benefits of Net Zero Water
Conservation of Freshwater Resources:
By maximizing the reuse of water, Net Zero Water systems drastically reduce the demand for freshwater. This is particularly crucial in areas facing water scarcity.
Reduction of Waste and Pollution:
These systems significantly lower the volume of wastewater entering sewage treatment facilities, reducing the risk of environmental contamination.
Sustainable Agriculture:
The use of filtered greywater and composted blackwater supports the cultivation of food forests and gardens, promoting biodiversity and sustainable food production.
Economic Savings:
Reduced reliance on municipal water supplies can lead to significant financial savings for households and communities. Additionally, the long-term benefits of a healthier ecosystem are immeasurable.
Resilience Against Climate Change:
Net Zero Water practices enhance local water security, making communities more resilient to droughts and other climate-related challenges.
Implementing Net Zero Water
Transitioning to a Net Zero Water system requires careful planning and investment. It starts with assessing water needs and available resources, followed by the installation of appropriate collection, storage, and treatment systems. Education and community involvement are key to ensuring the success and sustainability of these initiatives.
By embracing Net Zero Water practices, we can take a significant step toward a more sustainable and resilient future, where every drop of water is valued and wisely used. Join us in this journey towards water sustainability, for the health of our planet and future generations.
FAQ
Welcome to our Net Zero Water FAQ, a comprehensive resource designed to enlighten you about achieving sustainable water management and conservation practices.
Here, we delve into the principles of Net Zero Water, exploring innovative strategies, projects, and technologies aimed at balancing water consumption with replenishment.
Our FAQs provide insights into how communities, businesses, and individuals can contribute to water sustainability, highlighting successful initiatives and practical solutions for preserving our most vital resource.
Discover the path to water neutrality and the pivotal role it plays in fostering a sustainable future.
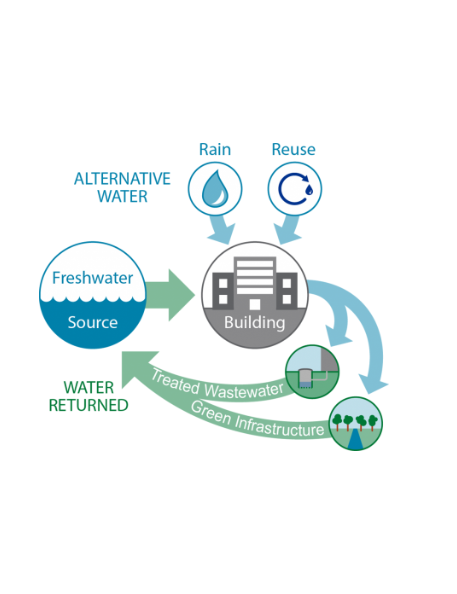
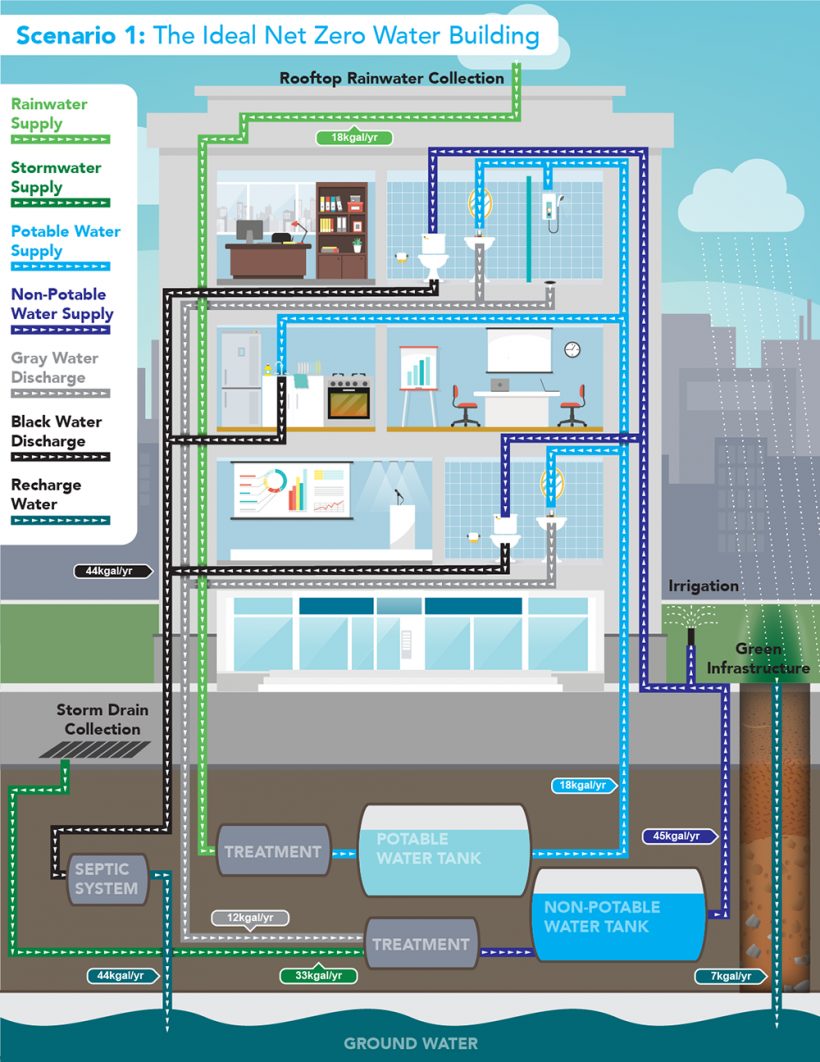
What is an Ideal Net Zero Water Building?
An ideal net zero water building is one that fully meets its water needs through the use of on-site alternative water sources. It treats all wastewater on-site and returns it to the original water source, ensuring no net water consumption.
This approach involves harvesting rainwater for potable uses, utilizing stormwater and graywater for non-potable demands, and implementing green infrastructure to recharge stormwater into the local aquifer.
How does a Mainstream Net Zero Water Building operate?
A mainstream net zero water building also aims for no net water consumption but might rely on a mix of municipal water and alternative sources.
It uses harvested rainwater and graywater for non-potable purposes, while potable water comes from municipal sources.
Wastewater is treated offsite at municipal facilities. Like the ideal scenario, it features green infrastructure for stormwater recharge.
What are the Key Design Elements of Net Zero Water Buildings?
Both ideal and mainstream net zero water buildings emphasize:
- Reducing water demand through innovative technologies that lower consumption.
- Producing alternative water sources to reduce the need for freshwater.
- Treating wastewater on-site for reuse or returning it to the water cycle.
- Employing green infrastructure to manage stormwater and replenish local water sources
What distinguishes an Ideal from a Mainstream Net Zero Water Building?
The primary distinction lies in their water sourcing and waste management strategies. The ideal scenario is fully self-sufficient, relying on on-site sources and treatment for all water needs and waste output. The mainstream scenario, however, combines on-site treatment of non-potable water with the use of municipal water for potable needs and may utilize municipal facilities for wastewater treatment.
What are the key objectives of the EPA's Net Zero Initiative?
The EPA’s Net Zero Initiative aims to assist communities and the military in achieving sustainability and resiliency goals across Net Zero Energy, Waste, and Water.
This initiative seeks to protect human health and the environment while generating societal and economic benefits by integrating and advancing science and technologies related to Net Zero/Net Positive strategies.
How do Net Zero and Net Positive strategies contribute to sustainability?
Net Zero and Net Positive (NZ/NP) strategies focus on reducing water, energy, and waste footprints in both installations and communities.
These strategies aim for long-term sustainability and resilience by ensuring environmental objectives such as clean air and water are met, waste sent to landfills is reduced or eliminated, and the long-term viability of resources is improved.
Essentially, they embody sustainability in action by balancing consumption with production and enhancing resource sustainability
Can you provide examples of successful Net Zero projects?
One notable project involved waste audits at rental properties, which revealed that about 75% of what was thrown away could be diverted through existing programs.
This led to the implementation of social marketing techniques aimed at reducing waste and encouraging recycling and composting.
Another project focused on aquifer recharge in partnership with the Army at Fort Irwin, exploring managed aquifer recharge as a strategy for local water conservation in areas prone to evaporation and water loss
How is Net Zero Water achieved in practice?
Achieving Net Zero Water involves limiting the consumption of water resources and ensuring that water is returned to the same watershed without depleting its quantity or quality over the year.
This balance helps maintain the watershed’s health and prevents long-term water scarcity, supporting both human needs and ecosystem sustainability.
What challenges and solutions are addressed in Net Zero Water projects?
Net Zero Water projects often tackle the challenges of water loss, contamination in recycling streams, and efficient waste management.
Solutions include innovative projects like aquifer recharge to conserve water, efforts to reduce contamination in recycling streams, and the use of technology to improve waste management practices.
These projects demonstrate practical approaches to achieving sustainability goals while also addressing specific environmental and operational challenges.